General Introduction of the JCM & the JCM-REDD+
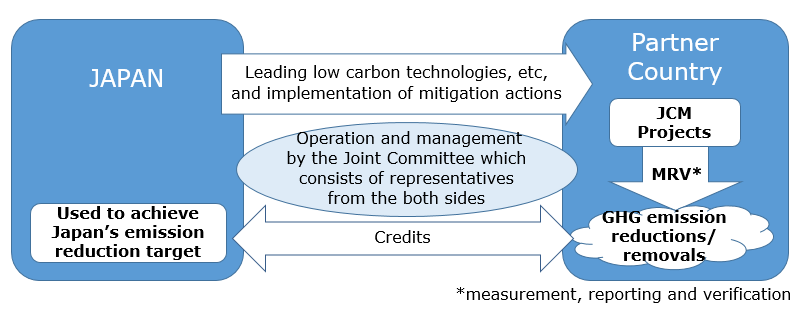
Basic Concept of the JCM
- Facilitating diffusion of leading low carbon technologies, products, systems, services, and infrastructure as well as implementation of mitigation actions, and contributing to sustainable development of developing countries.
- Appropriately evaluating contributions from Japan to GHG emission reductions or removals in a quantitative manner and use them to achieve Japan’s emission reduction target.
- Contributing to the ultimate objective of the UNFCCC by facilitating global actions for GHG emission reductions or removals.
About the JCM-REDD+
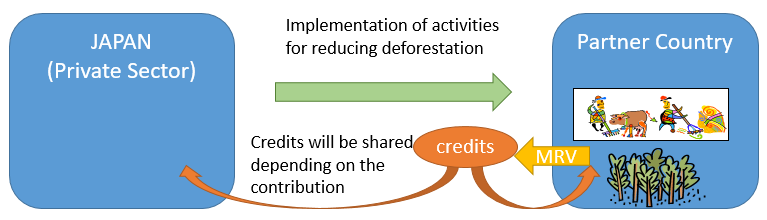
- REDD+ is one of the potential sector of the JCM.
- Japan contributes to reduce GHG emission through implementing REDD+ activities
- The JCM credits are shared
The credits are generated through MRV of the GHG emission reductions or removals achieved by the activities and shared among the project participants and/or both countries taking into consideration their contribution
 Features of the JCM-REDD+
Features of the JCM-REDD+
- Flexibility in rules
As the JCM is based on the bilateral documents, national circumstances can be reflected in the implementation rules
- Upfront funding
The JCM-REDD+ can provide upfront funding to implement REDD+ activities to reduce deforestation and/or forest degradation which is essential for achieving results
- Private sector involvement
The JCM-REDD+ aims for private sector participation in REDD+
- Rural development and poverty alleviation
JCM-REDD+ projects are expected to directly involve local communities and contribute to improving their livelihoods
For further information about JCM, please visit the web page: https://www.jcm.go.jp/kh-jp/about

